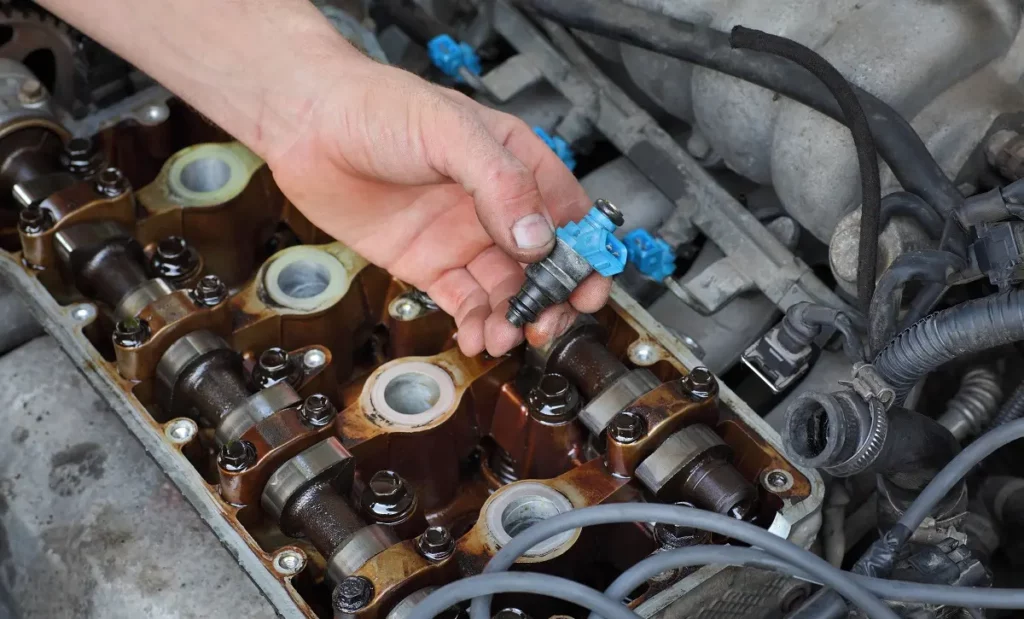
Diagnosing a bad fuel injector is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s performance. A faulty injector can lead to poor fuel efficiency, rough idling, and even engine damage. Here’s a simple guide to help you identify a bad injector.
First, look for symptoms of a failing injector. Common signs include rough engine performance, misfires, and a decrease in power. You may also notice a drop in fuel efficiency or a strong smell of fuel. If your engine struggles to start, it could indicate injector issues.
Next, conduct a visual inspection. Check the injector for leaks. Look around the injector body and the connection points. Fuel leaks can cause performance problems and need immediate attention.
Listen for unusual sounds. A functioning injector should produce a clicking noise during operation. If you hear nothing or a loud noise, it may be malfunctioning. Use a stethoscope or a screwdriver to listen closely to each injector.
Now, perform a resistance test. Disconnect the electrical connector from the injector. Use a multimeter to measure the resistance. Most injectors should read between 12 to 16 ohms. Values outside this range may indicate a bad injector.
Next, conduct a flow test. To do this, remove the injector from the engine and connect it to a fuel source. Measure how much fuel flows from it in a specific time, usually 15 seconds. A good injector will typically deliver 30-35 ml of fuel. If it delivers less, it may be clogged or damaged.
Additionally, check for electrical issues. Inspect the wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion. Faulty wiring can lead to injector failure. Fix any issues before concluding that the injector itself is the problem.
If you suspect the injector is faulty, replacement is necessary. Injector prices can vary widely. They typically range from $50 to $150 each, depending on the make and model of your vehicle. Labor costs for installation can add another $100 to $200.
In summary, diagnosing a bad fuel injector involves observing symptoms, conducting visual inspections, listening for sounds, performing resistance and flow tests, and checking electrical connections. If you find issues, replacing the injector is essential for proper vehicle function.
Understanding The Symptoms Of A Failing Fuel Injector: Key Signs To Watch For
Fuel injectors play a crucial role in your vehicle’s performance. They inject fuel into the engine, ensuring optimal combustion. When a fuel injector starts to fail, it can lead to several noticeable symptoms. Understanding these signs can help you diagnose the issue early and prevent further damage. Here are the key symptoms of a failing fuel injector.
1. Poor Engine Performance
If you notice a decrease in acceleration or a rough idle, it could be a sign of a bad fuel injector. A malfunctioning injector may not deliver the right amount of fuel, leading to poor engine performance.
2. Increased Fuel Consumption
Watch for a sudden increase in fuel usage. If your vehicle is consuming more gas than usual, a failing fuel injector may be to blame. Inefficient fuel delivery can cause your engine to work harder.
3. Engine Misfires
Frequent engine misfires can indicate an issue with one or more fuel injectors. When the injector does not spray fuel correctly, it can lead to incomplete combustion, causing the engine to misfire.
4. Rough Idle
A rough or shaky idle is another symptom. If your engine shakes or vibrates while idling, it could suggest an injector problem. This occurs when the fuel mixture is not balanced.
5. Unusual Noises
Listen for knocking or tapping noises from the engine. These sounds may arise from improper fuel delivery. A failing injector can create abnormal combustion noises.
6. Check Engine Light
If your check engine light illuminates, it’s time to investigate. This light can indicate a multitude of issues, including problems with the fuel injectors. Use an OBD-II scanner to check for related error codes.
7. Fuel Leaks
Inspect for fuel leaks around the injectors. If you see any puddles or smell fuel near the engine, you may have a leaking injector. This can be dangerous and should be addressed immediately.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Poor Engine Performance | Decreased acceleration and rough idle. |
| Increased Fuel Consumption | Sudden rise in fuel usage. |
| Engine Misfires | Irregular firing and power loss. |
| Rough Idle | Shaky engine when at rest. |
| Unusual Noises | Knocking or tapping from the engine. |
| Check Engine Light | Indicator of various engine issues. |
| Fuel Leaks | Puddles or fuel smell near injectors. |
Recognizing these symptoms early can save you time and money. If you experience any of these signs, it’s advisable to have your fuel injectors inspected. Timely diagnosis can lead to a smoother running engine and better fuel efficiency.
Essential Diagnostic Tools For Identifying Bad Fuel Injectors In Your Vehicle
Fuel injectors play a crucial role in your vehicle’s performance. If they malfunction, they can lead to poor fuel economy and reduced power. Identifying bad fuel injectors early can save you time and money on repairs. Here are essential diagnostic tools that can help you find injector problems.
First, consider using an OBD-II Scanner. This device connects to your vehicle’s onboard computer. It reads Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that can signal issues with the fuel injectors. Most OBD-II scanners cost between $30 to $150, depending on features.
Next, a Fuel Pressure Gauge is vital. This tool measures the fuel pressure in the system. If the fuel pressure is below the manufacturer’s specification, it may indicate a problem with the injectors. A good fuel pressure gauge typically ranges from $20 to $100.
Another useful tool is a Digital Multimeter. This device can check the electrical resistance of the fuel injectors. If the resistance is too high or too low, the injectors might be faulty. A decent digital multimeter is available for $10 to $50.
A Fuel Injector Tester is specifically designed for testing injectors. It helps to check if the injectors are firing properly. This tool can range from $50 to $200, depending on its complexity.
Lastly, a Vacuum Gauge can help diagnose engine performance issues. A vacuum gauge provides insights into the engine’s health and can indirectly point to injector problems. Prices for vacuum gauges typically range from $15 to $60.
| Tool | Function | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| OBD-II Scanner | Reads Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) | $30 – $150 |
| Fuel Pressure Gauge | Measures fuel pressure | $20 – $100 |
| Digital Multimeter | Checks electrical resistance | $10 – $50 |
| Fuel Injector Tester | Tests injector firing | $50 – $200 |
| Vacuum Gauge | Indicates engine performance | $15 – $60 |
In summary, using the right diagnostic tools is key to identifying bad fuel injectors. Each tool has its specific purpose and price range. By choosing the right equipment, you can efficiently diagnose injector issues and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly.
Step-by-Step Guide To Testing Fuel Injectors: Ensuring Optimal Engine Performance
Fuel injectors play a crucial role in your engine’s performance. They deliver the right amount of fuel at the right time. A faulty injector can lead to poor performance, reduced fuel efficiency, and increased emissions. This guide will help you test your fuel injectors step by step.
Testing fuel injectors is essential for maintaining optimal engine health. The process requires some basic tools and a clear understanding of the symptoms of a bad injector. Here’s how to diagnose a bad injector effectively.
First, recognize the symptoms of a faulty fuel injector:
- Engine misfires
- Poor acceleration
- High fuel consumption
- Excessive emissions
- Rough idling
Once you’ve identified these symptoms, follow these steps to test your fuel injectors:
Materials Needed:
- Multimeter
- Fuel pressure gauge
- Injector cleaning kit (optional)
- Safety goggles
- Rags for spills
Step 1: Safety First
Before starting, wear safety goggles. Ensure the engine is turned off and cool. Disconnect the battery to avoid any electrical issues.
Step 2: Inspect the Injectors
Visually check the fuel injectors for any signs of damage or leaks. Look for cracks, dirt, or fuel pooling around the injector. Clean the area gently if needed.
Step 3: Test Injector Resistance
Use a multimeter to check the resistance of each injector. Disconnect the electrical connector from one injector. Set the multimeter to ohms and connect the probes to the injector terminals. A typical resistance range is between 12 to 16 ohms. If the reading is outside this range, the injector may be faulty.
Step 4: Check Fuel Pressure
Connect a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel rail. Turn the ignition key to the on position without starting the engine. Check the pressure reading. Compare it with the manufacturer’s specifications. Normal fuel pressure is usually between 30 to 50 psi. If it’s lower, it may indicate a problem with the fuel pump or clogged filters.
Step 5: Perform an Injector Balance Test
For this test, you will need an injector cleaning kit or a specialized tool. This allows you to measure the flow rate of each injector. Remove the injectors and connect them to the cleaning kit. Activate the injectors and observe the flow. All injectors should have a similar spray pattern and volume. If one injector flows significantly less, it may be clogged or malfunctioning.
Step 6: Reassemble
After testing, carefully reassemble any components you removed. Reconnect the battery. Start the engine and observe how it runs. If issues persist, further investigation may be needed.
In summary, testing fuel injectors is vital for ensuring your engine runs smoothly. By following these steps, you can effectively diagnose a bad injector and take corrective action. Always remember to handle fuel and electrical components with care.
| Step | Task | Tools Needed |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Safety inspection | Safety goggles |
| 2 | Visual inspection | None |
| 3 | Test injector resistance | Multimeter |
| 4 | Check fuel pressure | Fuel pressure gauge |
| 5 | Perform balance test | Injector cleaning kit |
| 6 | Reassemble | None |
Following this guide will help you maintain optimal engine performance. Properly functioning fuel injectors are key to efficient operation and long-term vehicle health.
Common signs include poor engine performance, rough idling, decreased fuel efficiency, and increased emissions. If you notice these issues, it may indicate injector problems.
You can perform a visual inspection for leaks or damage, listen for clicking sounds while the engine is running, and use a multimeter to test the resistance of the injector coils.
Essential tools include a multimeter, a fuel pressure gauge, and possibly a stethoscope or a mechanic’s stethoscope to listen for injector operation sounds.
Yes, you can test their electrical operation and listen for clicks while the engine is running, but for thorough testing, removal may be necessary.
Yes, many injectors can be cleaned using specialized injector cleaning solutions or ultrasonic cleaning methods, although severely damaged injectors may need replacement.
A bad injector can cause misfires, poor acceleration, and rough running, leading to an overall decrease in performance and drivability.
Using a fuel pressure gauge, you can measure the fuel pressure at the injector rail; it should meet the specifications outlined in your vehicle’s service manual.
Common causes include dirt or debris in the fuel system, electrical issues, wear and tear over time, or prolonged exposure to poor-quality fuel.
Yes, a diagnostic scan tool can read DTCs that indicate injector malfunctions, misfires, or lean/rich fuel conditions, helping pinpoint issues.
While it’s not always necessary, replacing all injectors can be beneficial to maintain consistent performance and avoid future issues, especially if they have high mileage.